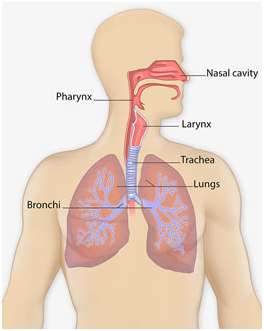
This illustration of the respiratory system shows the lungs, bronchi, trachea, larynx, pharynx, and nasal cavity.
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer.
Lung cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body, such as the brain. Cancer from other organs also may spread to the lungs. When cancer cells spread from one organ to another, they are called metastases.
Lung cancers usually are grouped into two main types called small cell and non-small cell. These types of lung cancer grow differently and are treated differently. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer.
What Are the Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
Coughing and chest pain may be symptoms of lung cancer.
Different people have different symptoms for lung cancer. Some people have symptoms related to the lungs. Some people whose lung cancer has spread to other parts of the body (metastasized) have symptoms specific to that part of the body. Some people just have general symptoms of not feeling well. Most people with lung cancer don’t have symptoms until the cancer is advanced. Lung cancer symptoms may include—
- Coughing that gets worse or doesn’t go away.
- Chest pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Wheezing.
- Coughing up blood.
- Feeling very tired all the time.
- Weight loss with no known cause.
Other changes that can sometimes occur with lung cancer may include repeated bouts of pneumonia and swollen or enlarged lymph nodes (glands) inside the chest in the area between the lungs.
These symptoms can happen with other illnesses, too. If you have some of these symptoms, talk to your doctor, who can help find the cause.
How Is Lung Cancer Diagnosed and Treated?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery.
Types of Lung Cancer
The two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. These categories refer to what the cancer cells look like under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer.
If you have lung cancer (especially non-small cell lung cancer), your doctor may run testsexternal icon to find out if you have a change in your genes (genetic mutation). The results of these tests help your doctor know which treatments will work best for you.
Staging
If lung cancer is diagnosed, other tests are done to find out how far it has spread through the lungs, lymph nodes, and the rest of the body. This process is called staging. The type and stage of lung cancer tells doctors what kind of treatment you need. For more information, visit Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancerexternal icon and Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer external icon
Types of Treatment
Lung cancer is treated in several ways, depending on the type of lung cancer and how far it has spread. People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.
- Chemotherapy. Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
- Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer.
- Targeted therapy. Using drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins.
Doctors from different specialties often work together to treat lung cancer. Pulmonologists are doctors who are experts in diseases of the lungs. Surgeons are doctors who perform operations. Thoracic surgeons specialize in chest, heart, and lung surgery. Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicines. Radiation oncologists are doctors who treat cancers with radiation.



